For coastal L.A., the hottest days of summer are yet to come
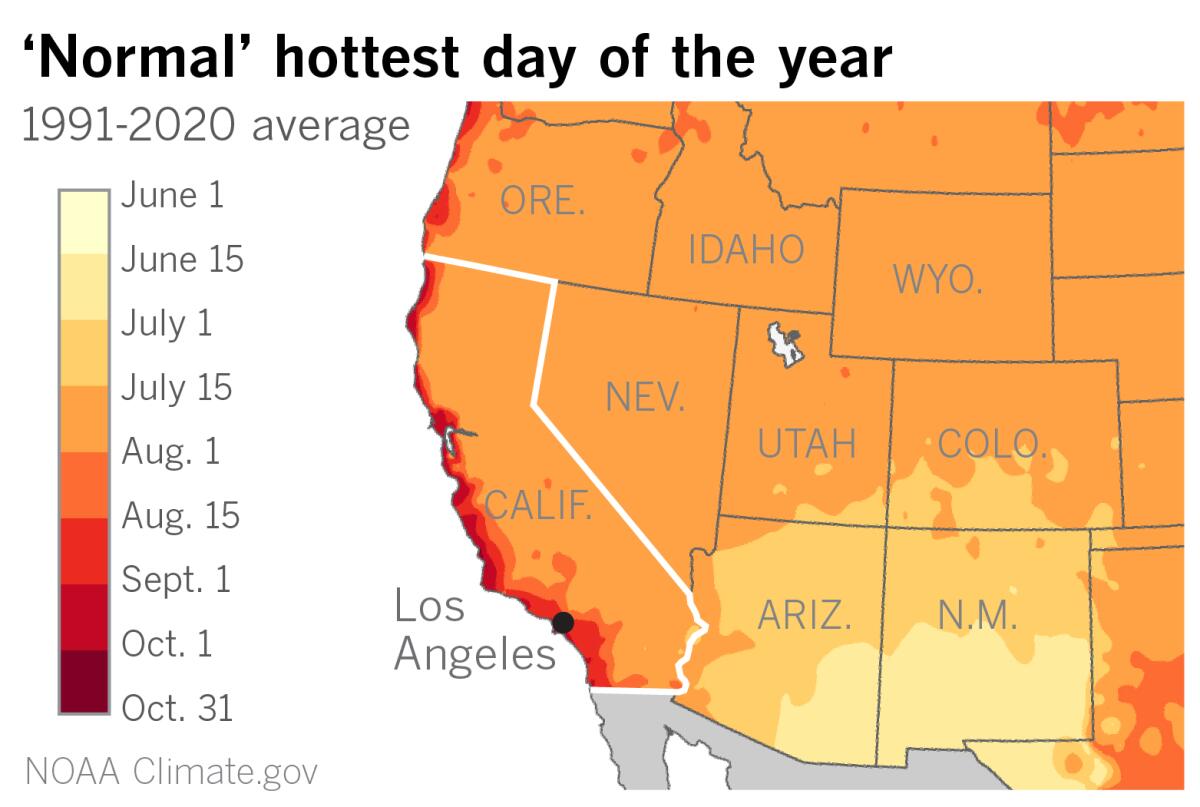
While stifling heat besieges the nation this weekend from the desert Southwest to the Northeast, coastal Californians can’t afford to be smug. The hottest weather of the season in the Southland is typically still to come, with all that portends for drought and fire weather conditions.
A strengthening upper-level ridge of high pressure stretching virtually from coast to coast is expected to bring excessive heat warnings across the country over the next few days, the National Weather Service said. The jet stream at this time of year has generally shifted to its farthest north location for the season, up near the Canadian border or beyond. This allows the most oppressive heat of the summer, on average, to occur under the ridge it forms to its south, across the contiguous U.S., from mid-July to early August.
But California is a slightly different story, largely depending on distance from the Pacific Ocean, thanks to a persistent marine layer. This gray layer of stratus clouds is generated by coastal waters chilled by the California Current flowing south from Alaska.
As the sun rose over the Sierra Nevada foothills, it appeared burnt orange through hazy skies in Mariposa County.
In Southern California, inland valleys are the hottest in mid-August, somewhat later than the rest of the country. Closer to the coast, the hottest weather is delayed just a fraction toward late August to Sept. 1, said Eric Boldt, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Oxnard. Some of the highest temperatures have occurred in September, due to offshore Santa Ana winds and downslope warming, he said.
Other parts of coastal California, especially north of Point Conception, don’t get their hottest average temperatures until even later. For example, Half Moon Bay sees its warmest average maximum temperatures in the second half of September and the first half of October, with almost all of its record readings in the low- to mid-90s occurring during those months.
But why don’t all the hottest days occur when the sun is at its most direct in the Northern Hemisphere? Solar radiation peaks with the summer solstice on June 21. The reason for the delay across most of the U.S. is that the rate of daytime heat input from the sun exceeds the cooling at night for several weeks after the solstice, until temperatures begin to taper off in late July and early August.
An increase in catastrophic wildfires has reduced California tree cover by 6.7% since 1985, and researchers fear the lost trees will never grow back.
Notable exceptions are Arizona and New Mexico, where the hottest weather tends to occur in June, before the rain clouds of the North American Monsoon typically gather. Thunderstorms usually bring cooler temperatures, and the monsoon, which peaks in July and early August, provides about half the annual rainfall for parts of the region. But in 2020, when the monsoon was essentially a no-show, the region endured record-shattering heat.
Another major exception is along the Pacific Coast, where the marine layer serves as a heat shield.
In summer, the West Coast is dominated by the Pacific High offshore and thermal low pressure over the continent, said Jan Null, a veteran Bay Area meteorologist with Golden Gate Weather Services. Air moves from high pressure toward lower pressure, creating moist northwest onshore winds moving down the California Coast, promoting marine layer clouds.
As we move into fall and winter, the pattern changes, Null said. The offshore high weakens and moves south, while at the same time the polar jet stream begins to dip south and bring cooler air masses and high pressure to the Great Basin.
This results in less protective marine-layer clouds for the coast, and temperatures begin to rise. The southward-dipping jet stream is a harbinger of cooler winter weather to come. But the building high pressure in the Great Basin also signals the start of Santa Ana season in Southern California, when the cool marine layer is banished and coastal temperatures soar.
In the fall and winter, the Great Basin, enclosed by mountain ranges, can be a huge tub of strong high-pressure air, all of which desperately wants to get out and flow toward lower pressure. That lower pressure can be found nearby, at sea level off the California coast. To get there, the high-pressure air will flow downslope and through passes and canyons. The atmosphere is constantly trying to restore equilibrium, and wind is associated with these changes in atmospheric pressure over short distances. So, once again, high pressure flows toward lower pressure, only this time it’s flowing offshore, generating Southern California’s infamous northeasterly Santa Ana winds.
The Great Basin’s valleys range in elevation from 2,000 to 6,000 feet. As this air descends toward the coast, it heats up and dries out due to compression. The sinking air increases in temperature by 5.5 degrees Fahrenheit for each 1,000 feet that it descends. This is called the lapse rate. Air that flows from a 4,500-foot mountain pass down to the ocean, for example, would warm by almost 25 degrees.
In addition to this difference in pressure, or pressure gradient, winds accelerate as they are squeezed through canyons and passes, creating a Venturi effect — much like a nozzle on a garden hose.
The offshore Santa Ana winds, at their strongest, can reach the coast and even Santa Catalina Island. They can hollow out waves, much to the delight of surfers. But even weaker offshore flow can restrict the marine layer. Now densely populated areas closer to the coast — that were able to hide from the heat under a blanket of marine clouds earlier in the season — are recording some of the highest temperatures.
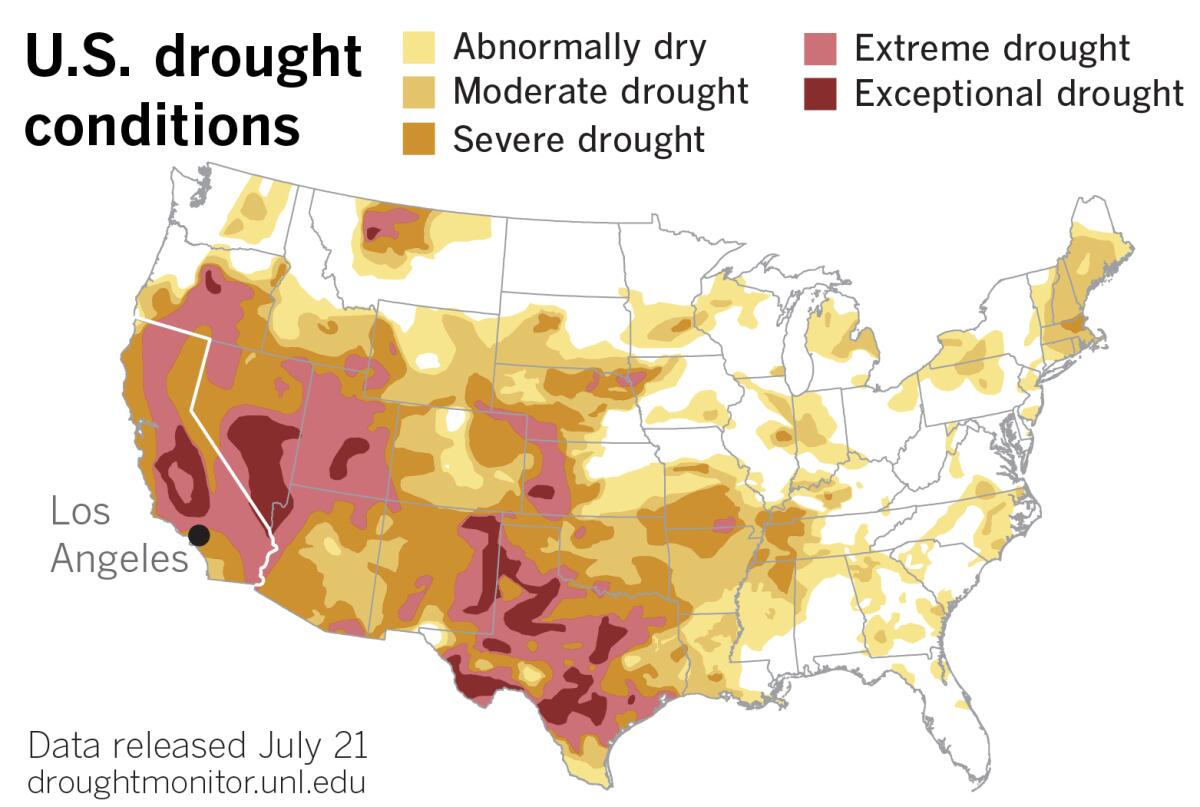
Even before the Santa Ana winds howl, coastal Southern California begins to see its marine-layer advantage deteriorate. Overnight minimum temperatures plateau at their highest average from about mid-July to mid-September, with many of L.A.’s record warmest overnight temperatures in the low- to mid-80s occurring in September. This means uncomfortable sleeping conditions for those too poor to afford air-conditioning. Those who can afford it strain the power grid by keeping their air-conditioners droning night and day.
Moreover, sea surface temperatures off Southern California, on average, peak in August and September, increasing humidity, Alex Tardy of the weather service’s San Diego office said. That, along with potential for moist monsoonal flow from the southeast, can keep both days and nights muggy.
While marine stratus clouds may provide a sunscreen for the coast, moderating temperatures when so many other places are baking, they usually bring only drizzle, at best, but no serious relief from California’s persistent drought. In a sense, with California’s Mediterranean climate and rain-free months, they save some of California’s worst heat for the end of the dry season when vegetation is most desiccated and fire-prone.
Each year, it’s a race to see which comes first, the beginning of the rainy season or the Santa Ana winds, as climatologist Bill Patzert, formerly of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, likes to point out.
La Niña, a global climate pattern which typically results in dry winters in the U.S. Southwest, is poised to continue into a rare third consecutive year. The pattern is expected to decrease during the July-September period before increasing again through the fall and winter, the National Weather Service’s Climate Prediction Center said earlier this month. So the odds look good that drought and elevated fire weather conditions are likely to persist — and worsen — into 2023.